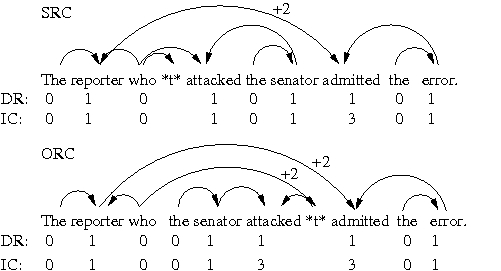
 "Integration Cost" is a concept from a psycholinguistic sentence
processing theory called Dependency Locality Theory (DLT; Gibson 1998;
2000), which estimates the difficulty of integrating a word with
previous context based on the distance of open dependencies to the
current word. For example, if we are processing a verb, and its
argument was processed a several words earlier (e.g. because of a
relative clause or multiple centre embedding structures that occurred
inbetween), it is going to be more difficult to integrate this
argument with our verb than if the argument had been the last word
before the verb. See for example the difference in Integration Cost
(IC) at the word "attacked" in the subject relative clause (SRC)
vs. the object relative clause (ORC) in the figure below. Distance
between a head and its argument are thereby measured in terms of
intervening discourse referents. In the SRC case, the integration cost
is lower because no discourse referents occur in between the argument
"who" and the head "attacked", while in the ORC case two discourse
referents "senator" and "attacked" itself occur at the point of
integrating "attacked" and the trace "*t*". For more details refer to
Gibson (2000).
"Integration Cost" is a concept from a psycholinguistic sentence
processing theory called Dependency Locality Theory (DLT; Gibson 1998;
2000), which estimates the difficulty of integrating a word with
previous context based on the distance of open dependencies to the
current word. For example, if we are processing a verb, and its
argument was processed a several words earlier (e.g. because of a
relative clause or multiple centre embedding structures that occurred
inbetween), it is going to be more difficult to integrate this
argument with our verb than if the argument had been the last word
before the verb. See for example the difference in Integration Cost
(IC) at the word "attacked" in the subject relative clause (SRC)
vs. the object relative clause (ORC) in the figure below. Distance
between a head and its argument are thereby measured in terms of
intervening discourse referents. In the SRC case, the integration cost
is lower because no discourse referents occur in between the argument
"who" and the head "attacked", while in the ORC case two discourse
referents "senator" and "attacked" itself occur at the point of
integrating "attacked" and the trace "*t*". For more details refer to
Gibson (2000).
Demberg and Keller 2008 have found evidence for integration cost effects on auxiliaries, when evaluating DLT integration cost (Gibson 1998, Gibson 2000) on a large eye-tracking corpus. The goal of this project is to follow up on this finding and test it in a laboratory setting running first a self-paced reading study, and afterwords, according to results and time constraints, an eye-tracking study.
References:
Data from Eye-tracking Corpora as Evidence for Theories of Syntactic Processing Complexity Vera Demberg and Frank Keller, 2008 In Cognition, Volume 109, Issue 2, pages 193-210
Gibson, E. (1998). Linguistic complexity: locality of syntactic dependencies. Cognition, 68, 1-76.
Gibson, E. (2000). Dependency locality theory: A distance-dased theory of linguistic complexity. In A. Marantz, Y. Miyashita, & W. O'Neil (Eds.), Image, language, brain: Papers from the first mind articulation project symposium (pp. 95-126). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.